What is PRP?
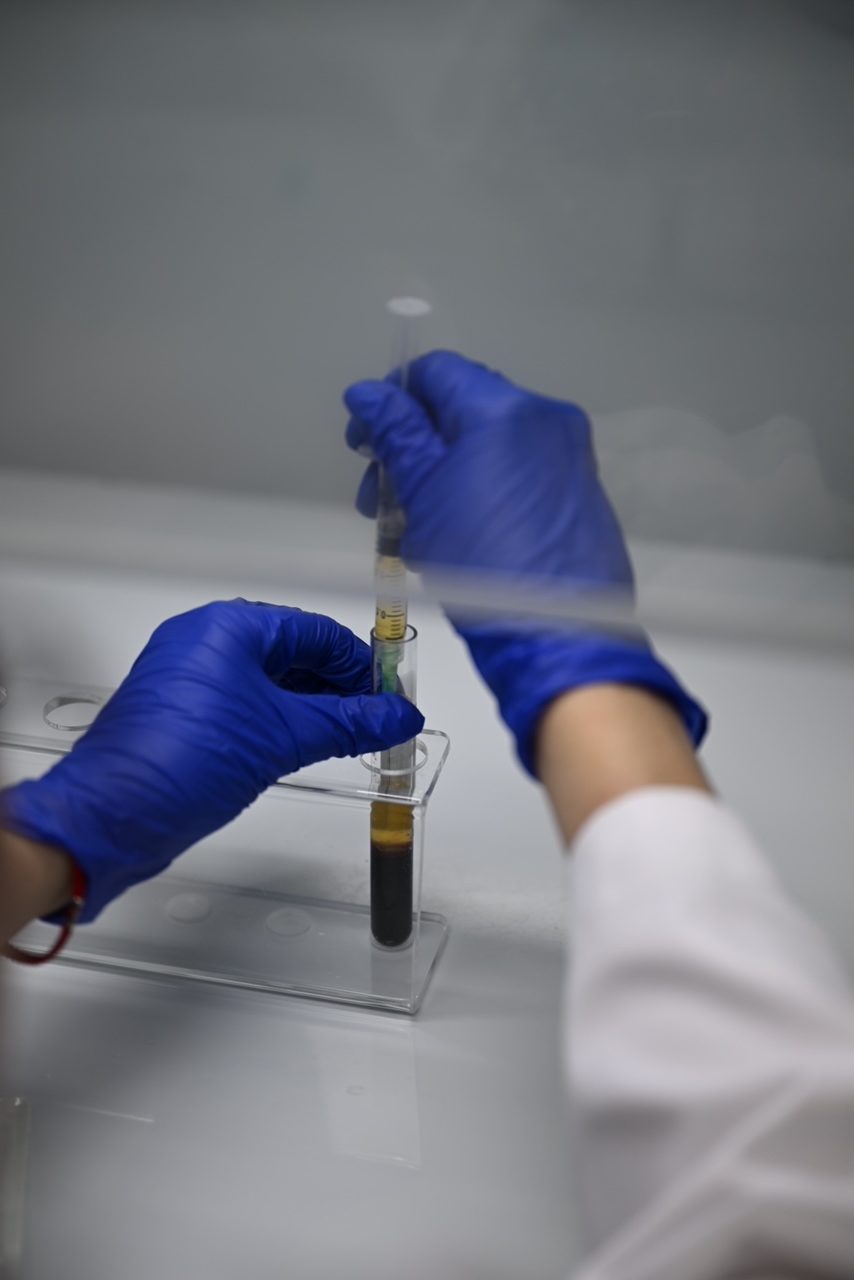
Platelet Rich Plasma (PRP) is a medical treatment that uses a patient’s own blood to promote healing. The blood is drawn from the patient, processed to concentrate the platelets, and then injected into the area of the body that needs to be treated. Platelets contain growth factors that promote healing and tissue regeneration. When injected into the body, PRP triggers a natural healing process that helps to reduce pain and improve function. PRP has been treat a variety of conditions including joint pain, sports injuries, and skin rejuvenation. The procedure is minimally invasive and has a low risk of side effects, making it an attractive option for patients seeking less invasive treatments.
Benefits
Reduced healing time
PRP has been shown to accelerate the healing process and reduce recovery time for a variety of conditions.
Non-invasive
PRP is a minimally invasive procedure that does not require surgery, making it a safe and attractive option for many patients.

Low risk of side effects
Because PRP uses a patient’s own blood, there is a low risk of side effects or allergic reactions.

Improved function
PRP has been shown to improve function and reduce pain in a variety of conditions, including joint pain and sports injuries.
Platelet Rich Plasma
Conditions that
can be treated
Joint pain: PRP is commonly used to treat joint pain, such as knee and hip pain, as well as conditions like osteoarthritis and tendonitis.
Sports injuries: PRP is frequently used to treat sports injuries, such as sprains, strains, and tears, and can help to reduce recovery time.
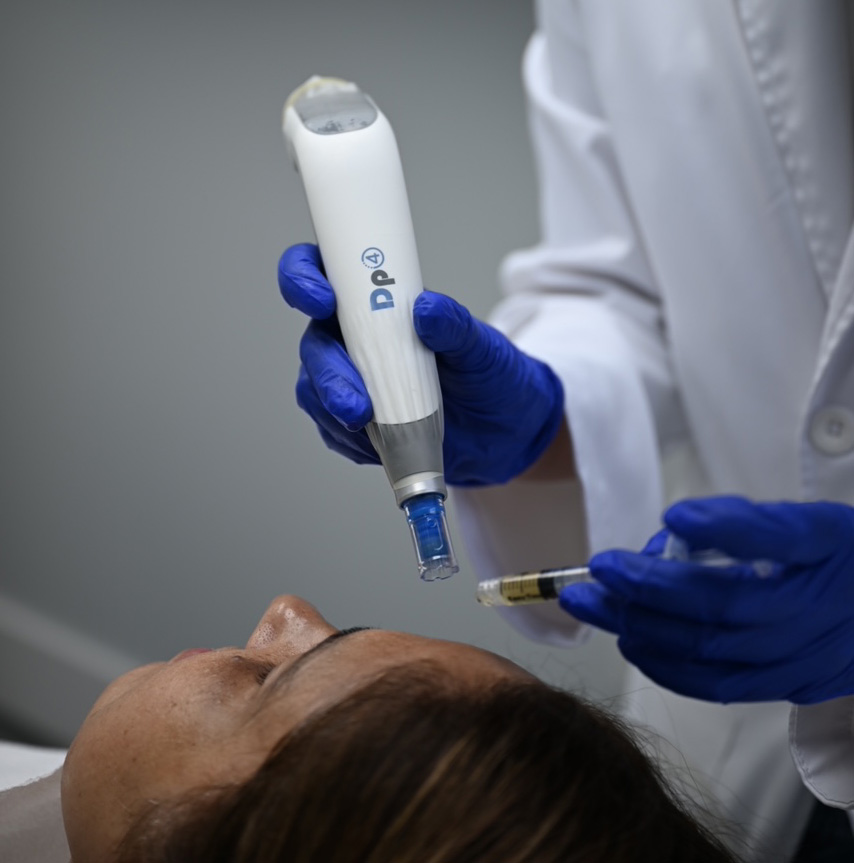
Skin rejuvenation: PRP is often used for skin rejuvenation, such as improving skin texture and reducing the appearance of fine lines and wrinkles.
Hair loss: PRP is a popular treatment for hair loss and promoting hair growth.
Chronic pain: PRP is commonly used to treat chronic pain, such as back pain and neck pain.
These are the most common uses for PRP, but it is being researched for its potential to treat a variety of other conditions.
Platelet Rich Plasma
PRP treatment process
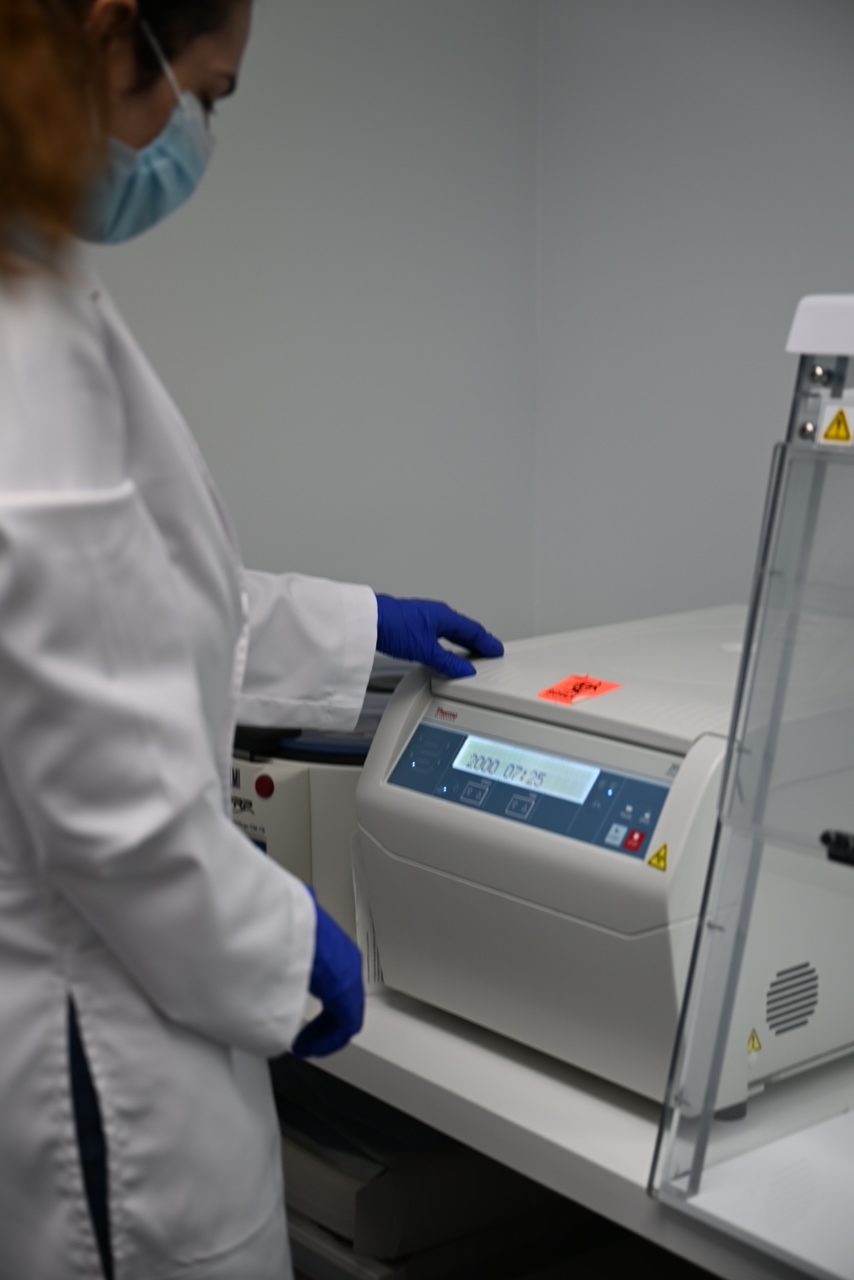
Blood draw: The first step in PRP treatment is to draw a small sample of blood from the patient.
Processing: The blood is then processed in a centrifuge to separate the platelets from the rest of the blood.
Concentrating platelets: The separated platelets are then further concentrated to create the PRP solution.
Injection: The PRP solution is then injected into the area of the body that needs to be treated. This can be done using a needle or other delivery method, depending on the specific condition being treated.
Post-treatment care: After the injection, patients may be instructed to rest and avoid physical activity for a period of time. Pain and swelling may occur, but can usually be managed with over-the-counter pain medications.